May Map of the Month
By: Grace Parker
Source by: American Community Survey
Unprecedented federal funding for underserved areas under the Justice 40 Initiative has the potential to mitigate the legacy of historical disinvestment in these communities. At the same time, new investments may contribute to gentrification if they fail to maintain the area’s affordability. Gentrification is the process by which lower-income households are displaced as their neighborhoods become less affordable—often due to rapidly rising rents or taxes —and it can be caused by the development of in-demand housing, businesses, and amenities. In many neighborhoods, this displacement disproportionately affects Black and Hispanic residents.
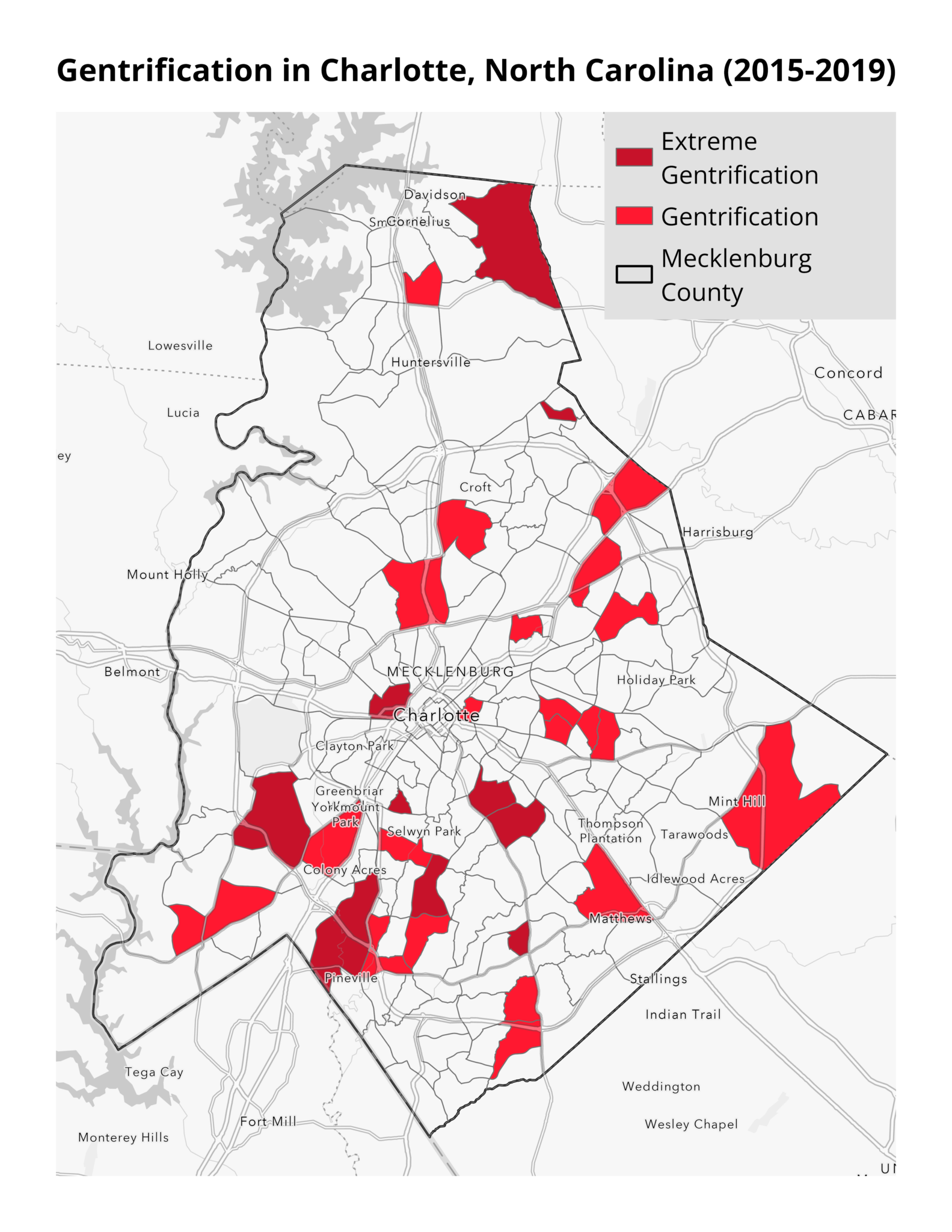
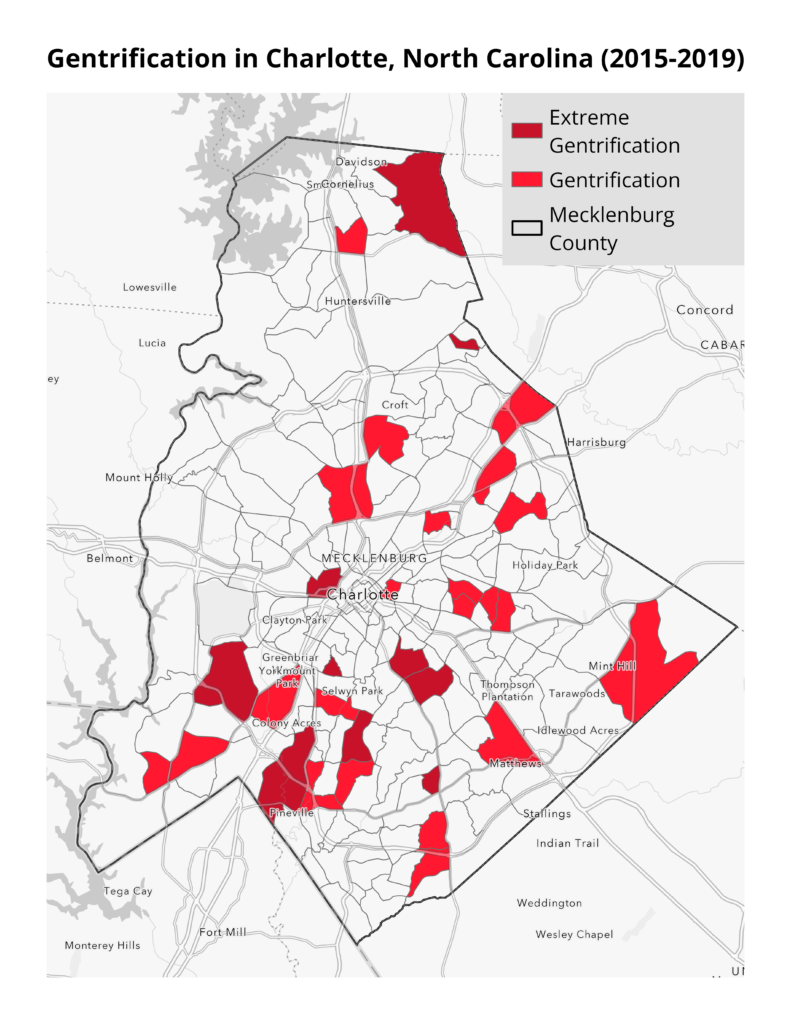
This month’s map highlights areas experiencing gentrification in Charlotte, North Carolina between 2015 and 2019. Our analysis finds that suburban communities in Charlotte have experienced the most rapid gentrification during this time. Areas like Davidson, Mint Hill, and Pineville have experienced sharp increases in the proportion of college-educated residents and in housing costs, for either renters or homeowners. In extremely gentrified tracts, on average, the proportion of college-educated residents increased by 9%, home values by 46%, and rental costs by 23% compared to 4%, 26%, and 18%, respectively, for lower-income tracts in general. It’s important to note that this method, created by Drexel University’s Urban Health Collaborative, of identifying gentrification does not take changes in racial composition into account, a component of other methods of identifying gentrification.
Gentrification is not unique to the South, but large Southern cities have experienced significant recent development that has put pressure on long-time residents. Our analysis focused on Charlotte as a case study of these booming Sunbelt cities that have been understudied, but other cities in the South—including Miami, New Orleans, and Nashville—are gentrifying even more rapidly.
Energy efficiency upgrades can help keep housing affordable by lowering energy costs and giving long-time residents savings that can be used to meet escalating housing costs. These measures are also important in enabling residents to pay for other necessities such as food and medicine and to prevent evictions.
Without careful design and execution, however, energy efficiency programs have the potential to increase the risk of gentrification by increasing rents and home values. This is sometimes called low-carbon gentrification.
Mechanisms to prevent low-carbon gentrification are critical and well-established. They can include agreements that prevent landlords from raising rents for a period after receiving energy efficiency upgrades. As Bipartisan Infrastructure Law and Inflation Reduction Act funding is invested in the Southeast, energy efficiency measures stand out as a mechanism to improve the quality of life in disinvested areas without displacing longstanding communities.



